Connecting through an HTTP proxy
Clients can connect to the Diffusion™ server through an HTTP proxy by using the HTTP CONNECT verb to create the connection and tunneling any of the supported transports through that connection.
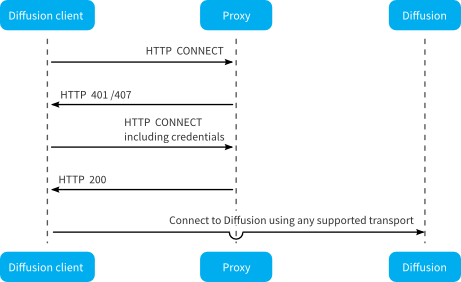
Apple® , Android™ , Java™ , and .NET clients can connect to the Diffusion server through an HTTP proxy by specifying additional information on connection.
With no authentication at the proxy
When creating your session, add an HTTP proxy to the session by passing in the host and port number of the proxy.
Diffusion.sessions().httpProxy(host, port)
var session = Diffusion.Sessions
.HttpProxy("proxy", 80)
.Open(serverUrl);
final Session session = Diffusion
.sessions()
.httpProxy("proxyHost", 80)
.open("ws://localhost:8080");
// Create an unauthenticated HTTP proxy configuration
let proxy_configuration = PTDiffusionHTTPProxyConfiguration(host: "proxy", port: 80)
// Create a mutable session configuration
let configuration = PTDiffusionMutableSessionConfiguration()
configuration.httpProxyConfiguration = proxy_configuration
// Use the configuration to open a new session...
PTDiffusionSession.open(with: URL(string: "wss://push.example.com")!,
configuration: configuration) { (session, error) in
// Check error is `nil`, then use session as required.
// Ensure to maintain a strong reference to the session beyond the lifetime
// of this callback, for example by assigning it to an instance variable.
if (session == nil) {
print("Failed to open session: %@", error!.localizedDescription)
return
}
// At this point we now have a connected session.
print("Connected.")
}
With basic authentication at the proxy
If the proxy requires basic authentication, the client can use the implementation in the Diffusion API to authenticate.
When creating your session, add an HTTP proxy to the session by passing in the host and port number of the proxy and a proxy authentication object that provides the challenge handler for basic authentication.
var clientAuth = Diffusion.ProxyAuthentication.Basic("username", "password");
var session = Diffusion.Sessions
.HttpProxy("proxy", 80, clientAuth)
.Open(serverUrl);
final HTTPProxyAuthentication auth =
Diffusion.proxyAuthentication().basic("username", "password");
final Session session = Diffusion
.sessions()
.httpProxy("proxyHost", 80, auth)
.open("ws://localhost:8080");
// Create an authentication provider for the HTTP proxy
let proxy_authentication = PTDiffusionBasicHTTPProxyAuthentication(username: "user",
password: "password")
// Create an unauthenticated HTTP proxy configuration using the provider
let proxy_configuration = PTDiffusionHTTPProxyConfiguration(host: "proxy",
port: 80,
authentication: proxy_authentication)
// Create a mutable session configuration
let configuration = PTDiffusionMutableSessionConfiguration()
configuration.httpProxyConfiguration = proxy_configuration
// Use the configuration to open a new session...
PTDiffusionSession.open(with: URL(string: "wss://push.example.com")!,
configuration: configuration) { (session, error) in
// Check error is `nil`, then use session as required.
// Ensure to maintain a strong reference to the session beyond the lifetime
// of this callback, for example by assigning it to an instance variable.
if (session == nil) {
print("Failed to open session: %@", error!.localizedDescription)
return
}
// At this point we now have a connected session.
print("Connected.")
}
With another form of authentication at the proxy
If the proxy requires another form of authentication, the client can implement a challenge handler that the client uses to authenticate.
Implement the HTTPProxyAuthentication interface to provide a challenge handler that can handle the type of authentication your proxy uses. When creating your session, add an HTTP proxy to the session by passing in the host and port number of the proxy and a proxy authentication object that provides your challenge handler.