Sending request messages to a message path
A client session can send a request message containing typed data to a message path. One or more client sessions can register to handle messages sent to that message path. The handling client session can then send a response message containing typed data. The response message is sent to the requesting client session directly, through the same message path.
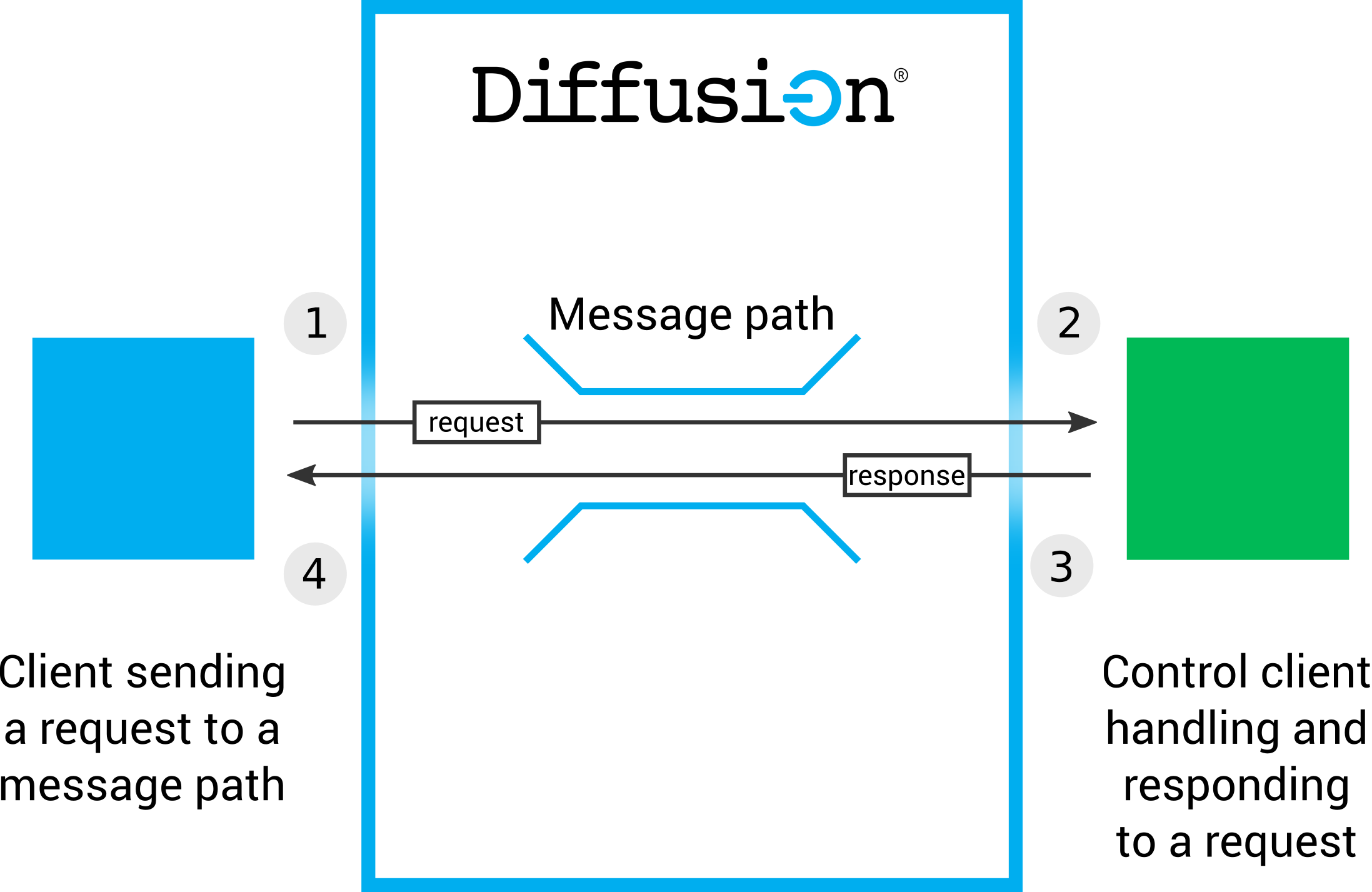
- A client session sends a request message to a message path.
- The control client session receives the request message through a request handler.
- The session client session uses sends a response to the request message.
- The client session receives the response.
Both the request message and the response message contain typed values. The messages can contain data of one of the following types: JSON, binary, string, 64-bit integer, or double. The response message is not required to be the same data type as the request it responds to.
Sending to a message path
Required permissions: permission for the specified message path
- The message path to send the request to and receive the response through
- The request message
- The datatype of the request message
- The datatype of the response message
// Example with json topic type.
const jsonType = diffusion.datatypes.json();
// Create a JSON object to send as a request.
const requestJson = jsonType.from('hello');
try {
// Send the request to a message path 'foo'.
const response = await control.messages.sendRequest('foo', requestJson, jsonType);
console.log(response.get());
} catch (err) {
console.log('An error occured');
}
/// <summary>
/// Client implementation that sends request messages to a path and
/// displays the response.
/// </summary>
public sealed class SendingPathRequestMessages {
public async Task SendingPathRequestMessagesExample(string serverUrl) {
var session = Diffusion.Sessions.Principal("control").Password( "password" )
.CertificateValidation((cert, chain, errors) => CertificateValidationResult.ACCEPT)
.Open(serverUrl);
var messaging = session.Messaging;
string messagingPath = ">random/requestResponse";
try {
string response = await messaging.SendRequestAsync<string, string>(
messagingPath, "Starting chat..." );
WriteLine( $"Received response: '{response}'." );
Thread.Sleep( 1000 );
response = await messaging.SendRequestAsync<string, string>(
messagingPath, "Hello!" );
WriteLine( $"Received response: '{response}'." );
}
catch ( Exception e )
{
WriteLine( $"Got exception: '{e.Message}'." );
}
// Close the session
session.Close();
}
}
//Establish client session
final Session session = Diffusion.sessions().open("ws://localhost:8080");
//Obtain the Messaging feature
final Messaging messaging = session.feature(Messaging.class);
//Create a JSON object to send as a request
final JSON request = Diffusion.dataTypes().json().fromJsonString("\"hello\"");
//Send the request to a message path "foo" and wait for (at most) 5 seconds until the response is received.
final JSON response = messaging.sendRequest("foo", request, JSON.class, JSON.class).get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
BUF_T *message_buf = buf_create();
write_diffusion_string_value(message, message_buf);
SEND_REQUEST_PARAMS_T params = {
.path = message_path,
.request = message_buf,
.on_response = on_message_response,
.request_datatype = DATATYPE_STRING,
.response_datatype = DATATYPE_STRING};
send_request(session, params);
buf_free(message_buf);
# Sending the request and receiving the response.
print(f"Sending request: '{request}' to path '{path}'...")
try:
response = await session.messaging.send_request_to_path(
path=path, request=request_type(request)
)
except diffusion.DiffusionError as ex:
print(f"ERROR: {ex}")
else:
print(f"... received response '{response}'")
let json_request = try! PTDiffusionJSON(jsonString: "{\"hello\": \"world\"}").request
session.messaging.send(json_request, toPath: message_path) { (response: PTDiffusionJSON?, error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Failed to send message to %@. Error: %@", message_path, error!.localizedDescription)
}
else {
print("Received response: %@", response!)
}
}
Responding to request messages sent to a message path
Required permissions: permission for the specified message path, permission, and permission to register to receive session property values with the request message
Define a request handler to receive and respond to request messages that have a specific data type.
const jsonType = diffusion.datatypes.json();
const responseJson = jsonType.from({ "ying": "yang"});
// Define a request handler for json topic type
const handler = {
onRequest: (request, context, responder) => {
responder.respond(responseJson, jsonType);
},
onError: () => {
// an error occured
},
onClose: () => {
// the handler is closed
}
};
/// <summary>
/// A simple IRequestHandler implementation that prints confirmation of the actions completed.
/// </summary>
internal class SimpleRequestHandler : IRequestHandler<string, string> {
/// <summary>
/// Indicates that the request handler was closed.
/// </summary>
public void OnClose()
=> WriteLine( "A request handler was closed." );
/// <summary>
/// Indicates that the request handler has received error.
/// </summary>
public void OnError( ErrorReason errorReason )
=> WriteLine( $"A request handler has received error: '{errorReason}'." );
/// <summary>
/// Indicates that a request was received and responds to it.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>On invalid request you would call: <see cref="IResponder{TResponse}.Reject(string)"/>.</remarks>
public void OnRequest( string request, IRequestContext context, IResponder<string> responder ) {
WriteLine( $"Received request: '{request}'." );
responder.Respond( DateTime.UtcNow.ToLongTimeString() );
}
}
private static final class JSONRequestHandler implements Messaging.RequestHandler<JSON, JSON> {
@Override
public void onRequest(JSON request, RequestContext context, Responder<JSON> responder) {
final JSON response = Diffusion.dataTypes().json().fromJsonString("\"world\"");
responder.respond(response);
}
@Override
public void onClose() {
}
@Override
public void onError(ErrorReason errorReason) {
}
}
static int on_message_response(
DIFFUSION_DATATYPE response_datatype,
const DIFFUSION_VALUE_T *response,
void *context)
{
// read the `response` by converting it to the datatype `response_datatype`
return HANDLER_SUCCESS;
}
def callback(request: typing.Optional[str], **kwargs) -> str:
return f"Hello there, {request}!"
class JSONRequestHandler: PTDiffusionJSONRequestDelegate {
func diffusionTopicTreeRegistration(_ registration: PTDiffusionTopicTreeRegistration,
didReceiveRequestWith json: PTDiffusionJSON,
context: PTDiffusionRequestContext,
responder: PTDiffusionResponder) {
print("Received request: %@", json)
let json_response = try! PTDiffusionJSON(jsonString: "{\"greetings\": \"stranger\"}").response
responder.respond(with: json_response)
}
func diffusionTopicTreeRegistrationDidClose(_ registration: PTDiffusionTopicTreeRegistration) {
print("Message path is now closed")
}
func diffusionTopicTreeRegistration(_ registration: PTDiffusionTopicTreeRegistration,
didFailWithError error: Error) {
print("Message path failed with error: %@", error.localizedDescription)
}
}
Register the request handler against a message path. You can only register one request handler against each message path.
const handler = {
onRequest: (request, context, responder) => {
// request received
},
onError: () => {
// an error occured
},
onClose: () => {
// the handler is closed
}
};
session.messages.addRequestHandler('topic', handler);
/// <summary>
/// Client implementation that registers a handler to listen for messages on a path.
/// </summary>
public sealed class ReceivingPathRequestMessages {
public async Task ReceivingPathRequestMessagesExample(string serverUrl) {
var session = Diffusion.Sessions.Principal( "control" ).Password( "password" )
.CertificateValidation((cert, chain, errors) => CertificateValidationResult.ACCEPT)
.Open(serverUrl);
var messaging = session.Messaging;
string messagingPath = ">random/requestResponse";
var requestHandler = new SimpleRequestHandler();
var requestHandlerRegistration = await messaging.AddRequestHandlerAsync(
messagingPath, requestHandler );
try {
Thread.Sleep( 60000 );//wait for messages...
} finally {
// Close session
await requestHandlerRegistration.CloseAsync();
session.Close();
}
}
}
messaging.addRequestHandler("foo", JSON.class, JSON.class, new JSONRequestHandler());
static int on_request_handler_active(
SESSION_T *session,
const char *path,
const DIFFUSION_REGISTRATION_T *registered_handler)
{
// message path `path` is now active for `registered_handler`
return HANDLER_SUCCESS;
}
static int on_request_received(
SESSION_T *session,
DIFFUSION_DATATYPE request_datatype,
const DIFFUSION_VALUE_T *request,
const DIFFUSION_REQUEST_CONTEXT_T *request_context,
const DIFFUSION_RESPONDER_HANDLE_T *handle,
void *context)
{
// handle request received
// and response to request with
// `diffusion_respond_to_request(session, handle, response, NULL)`
return HANDLER_SUCCESS;
}
void register_request_handler(
SESSION_T *session,
char *message_path)
{
DIFFUSION_REQUEST_HANDLER_T request_handler = {
.request_datatype = DATATYPE_STRING,
.response_datatype = DATATYPE_STRING,
.on_active = on_request_handler_active,
.on_request = on_request_received};
ADD_REQUEST_HANDLER_PARAMS_T params = {.path = message_path, .request_handler = &request_handler};
add_request_handler(session, params);
}
# Register handler to receive the request
handler = RequestHandler(
callback,
request_type=request_type,
response_type=request_type
)
print("Registering request handler...")
try:
await session.messaging.add_request_handler(path, handler=handler)
except diffusion.DiffusionError as ex:
print(f"ERROR: {ex}")
else:
print("... request handler registered")
let handler = JSONRequestHandler()
let request_stream = PTDiffusionJSON.requestHandler(with: handler)
session.messaging.add(request_stream, forPath: message_path) { (registration, error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("An error has occurred while registering the message path %@. Error: %@",
message_path, error!.localizedDescription)
}
else {
print("Message path %@ has been successfully registered.", message_path)
}
}