Session lifecycle
When a client connects to Diffusion® Cloud, the instance of the connection is called a session. This topic provides details about the various session states, their typical life-cycle, and reconnection options.
Session state
A session is different to a connection. If a client becomes temporarily disconnected from the Diffusion® Cloud service, it can reconnect and continue using the same session.
Diffusion® Cloud reconnects losslessly. This means that while the connection is broken, pending updates are stored in recovery buffers. If the session can’t reconnect without losing data, it terminates instead.
The possible (typical) states a session can be in are as follows:
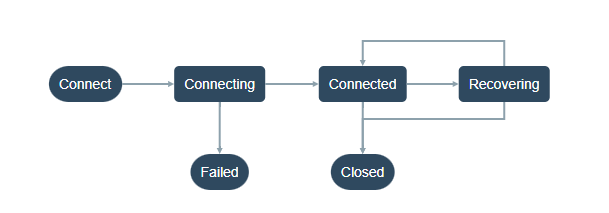
Monitoring session states
When your client has opened a session with Diffusion® Cloud, you can be notified about session events, when the session state changes.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
connected |
The session has successfully connected to Diffusion® Cloud |
disconnected |
The client is disconnected, and will attempt to reconnect (if enabled) |
reconnect |
The client has reconnected to Diffusion® Cloud |
close |
The session is closed (terminal) |
error |
The session encountered an error (terminal) |
session.addListener(new Listener() {
@Override
public void onSessionStateChanged(Session session, State oldState,
State newState) {
LOG.info("Session state changed from {} to {}", oldState, newState);
}
});session.on({
disconnect: () => {
console.log('Session disconnected');
},
reconnect: () => {
console.log('Session reconnected');
},
close: () => {
console.log('Session closed');
},
error: () => {
console.log('An error occurred');
}
});private void OnSessionStateChanged(object sender, SessionListenerEventArgs e)
{
WriteLine($"Session state changed from {e.OldState} to {e.NewState}.");
}
...
string url = "<url>";
string principal = "<principal>";
string password = "<password>";
var factory = Diffusion.Sessions
.Principal(principal)
.Credentials(Diffusion.Credentials.Password(password))
.SessionStateChangedHandler(OnSessionStateChanged);
ISession session = factory.Open(url);
WriteLine($"Connected to Diffusion via session {session}.");static void on_session_state_changed(
SESSION_T *session,
const SESSION_STATE_T old_state,
const SESSION_STATE_T new_state)
{
printf("Session state changed from %s (%d) to %s (%d)\n",
session_state_as_string(old_state), old_state,
session_state_as_string(new_state), new_state);
}
...
CREDENTIALS_T *credentials = credentials_create_password("<password>");
DIFFUSION_ERROR_T error = { 0 };
SESSION_LISTENER_T session_listener = {
.on_state_changed = &on_session_state_changed
};
SESSION_T *session = session_create(
"<url>",
"<principal>",
credentials,
&session_listener,
NULL,
&error);NotificationCenter.default.addObserver(
forName: NSNotification.Name.PTDiffusionSessionStateDidChange,
object: session,
queue: nil) { (notification) in
let change = notification.userInfo![PTDiffusionSessionStateChangeUserInfoKey]! as! PTDiffusionSessionStateChange
print("Session state changed from %@ to %@", change.previousState, change.state)
}Reconnection
Diffusion® Cloud keeps client sessions in the DISCONNECTED state for a maximum of 60 seconds.
During this time, the client can reconnect to the same session and receive any missed messages.
By default, clients have reconnection enabled by default. The default behaviour is to try to reconnect every 5 seconds, starting 5 seconds after the connection is lost. This behaviour is configurable through custom reconnection strategies.
Configuring client reconnection
To lower reconnection timeout than the default of 60 seconds, specify it when you create the session:
final Session session = Diffusion
.sessions()
.reconnectionTimeout(30000)
.open(url);const options: diffusion.Options = {
host: '<url>',
principal: '<principal>',
credentials: '<password>',
reconnect: 30
};
const session = await diffusion.connect(options);
console.log(`Connected to Diffusion via session ${session.sessionId}`);string url = "<url>";
string principal = "<principal>";
string password = "<password>";
var factory = Diffusion.Sessions
.Principal(principal)
.Credentials(Diffusion.Credentials.Password(password))
.ReconnectionTimeout(30);
ISession session = factory.Open(url);
WriteLine($"Connected to Diffusion via session {session}.");CREDENTIALS_T *credentials = credentials_create_password("<password>");
const long retry_count = 30;
const long retry_delay = 1;
const long timeout = 30;
RECONNECTION_STRATEGY_T *reconnection_strategy =
make_reconnection_strategy_repeating_attempt(retry_count, retry_delay);
reconnection_strategy_set_timeout(reconnection_strategy, timeout);
SESSION_T *session = session_create(
"<url>",
"<principal>",
credentials,
NULL,
reconnection_strategy,
NULL);let url = URL.init(string: "<url>")!
let configuration = PTDiffusionMutableSessionConfiguration()
configuration.principal = "<principal>"
configuration.credentials = PTDiffusionCredentials.init(password: "<password>")
configuration.reconnectionTimeout = 30;
PTDiffusionSession.open(with: url, configuration: configuration) { (session, error) in
print("Connected to Diffusion via session %@", session!)
}Disabling reconnection
While automatic reconnection is useful for most types of applications, you can disable reconnection if you wish to.
For instance, if you have a back-end service that has registered a message handler or session lock, keeping the session in a DISCONNECTED state can lead to unresponsive behaviour.
It’s often preferable for these types of clients to close fully and restart as a new session.
To disable reconnection, set the reconnection timeout to 0 when establishing a session:
final Session session = Diffusion
.sessions()
.reconnectionTimeout(0)
.open(url);const options: diffusion.Options = {
host: '<url>',
principal: '<principal>',
credentials: '<password>',
reconnect: 0
};
const session = await diffusion.connect(options)
console.log(`Connected to Diffusion via session ${session.sessionId}`)string url = "<url>";
string principal = "<principal>";
string password = "<password>";
var factory = Diffusion.Sessions
.Principal(principal)
.Credentials(Diffusion.Credentials.Password(password))
.ReconnectionTimeout(0);
ISession session = factory.Open(url);
WriteLine($"Connected to Diffusion via session {session}.");CREDENTIALS_T *credentials = credentials_create_password("<password>");
RECONNECTION_STRATEGY_T *reconnection_strategy =
make_reconnection_strategy_repeating_attempt(0, 0);
reconnection_strategy_set_timeout(reconnection_strategy, 0);
SESSION_T *session = session_create(
"<url>",
"<principal>",
credentials,
NULL,
reconnection_strategy,
NULL);let url = URL.init(string: "<url>")!
let configuration = PTDiffusionMutableSessionConfiguration()
configuration.principal = "<principal>"
configuration.credentials = PTDiffusionCredentials.init(password: "<password>")
configuration.reconnectionTimeout = 0;
PTDiffusionSession.open(with: url, configuration: configuration) { (session, error) in
print("Connected to Diffusion via session %@", session!)
}Setting a custom reconnection strategy
If you want more control over client reconnection behaviour, you can specify a custom reconnection strategy.
This enables you to specify what the client should do when it enters the RECOVERING_RECONNECT state.
| Even if you use a custom reconnection strategy, client sessions are only available for reconnection, for a maximum of 60 seconds. |
Examples of implementing a custom reconnection strategy are available in our GitHub examples repository.